Researchers in Japan have created a high-performance heterogeneous catalyst for the oxidative functionalization of C-H bonds in alkylarene compounds, an essential step in the production of solvents, polymers, surfactants, agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. The catalyst, made of isolated manganese (Mn) species fixed in a crystalline matrix, requires only mild reaction conditions — 40°C and atmospheric pressure. The work already has drawn the attention of several Japanese chemical companies.
“They are interested in the concepts of a simple catalyst synthesis method and the versatility of combined elements, and we have just started joint research on applying the method to important reactions,” confirms research leader Keigo Kamata, an associate professor at the Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan.
Kamata and his team built on their earlier studies into the catalytic properties of Mg6MnO8, a rock-salt structure of magnesium oxide (MgO). However, this time, they used a cost-effective sol-gel process aided by malic acid to create Mg6MnO8 with a specific surface area of 104 m2/g. “That’s about seven times higher than Mg6MnO8 synthesized using previously reported methods,” explains Kamata.
The new catalyst boasts a higher yield than existing Mn-based catalysts and the added benefits of easy recovery by filtration and no loss of activity even after multiple cycles.
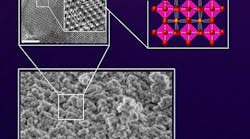
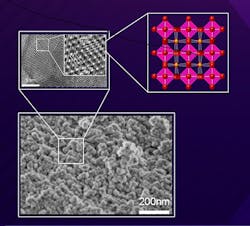
Figure 1. Isolated Mn4+ species located in a basic MgO matrix were found to play an important role in C-H bond functionalization. Source: Tokyo Tech.
To understand why this is the case, the team then investigated the correlation between the reactivity and acidity of the substrates and the kinetic isotope effects (KIEs) used to determine reaction mechanisms.
These studies, in combination with 18O-labeling experiments, showed that hydrogen abstraction from the hydrocarbon proceeds via a mechanism involving O2 activation. The structure of Mg6MnO8 consisting of isolated Mn4+ species located in a basic MgO matrix (Figure 1) was found to play an important role in this oxidation process.
Kamata believes this approach is a promising strategy for developing highly efficient heterogeneous oxidation systems with wide substrate scopes and, so, could pave the way to more efficient and environmentally friendly catalysts for organic chemistry applications.
Because the nanomaterials used can be easily synthesized by the simple calcination of precursors, he reckons scaling-up catalyst synthesis is possible.
“On the other hand, however, it is a problem that catalyst pretreatment is required when applying it to the liquid-phase oxidation reaction; thus, the catalytic application to gas-phase reactions at high temperature would be more suitable,” Kamata concludes.