Light Splits Water
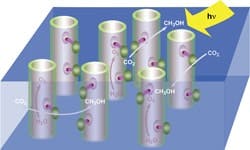
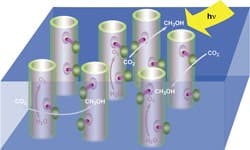
Light coupled with an inorganic catalyst can efficiently produce oxygen from water, report researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, Calif. The technology will play an essential part in making liquid fuels using sunlight, they hope. "Photo-oxidation of water molecules into oxygen, electrons and protons (hydrogen ions) is one of the two essential half reactions of an artificial photosynthesis system — it provides the electrons needed to reduce carbon dioxide to a fuel," explains Heinz Frei, senior scientist at the lab, who worked on the development with Feng Jiao. "Effective photo-oxidation requires a catalyst that is both efficient in its use of solar photons and fast enough to keep up with the solar flux in order to avoid wasting those photons. Clusters of cobalt oxide (Co3O4) nanocrystals are sufficiently efficient and fast, and also are robust and abundant. They perfectly fit the bill." The researchers achieved efficient oxygen generation at mild conditions — room temperature, a modest over-potential of 350 mV, and a pH of 5.8 (required for the visible light sensitizer rather than the catalyst). The tests, which ran for several hours, indicated no degradation in catalytic activity. "The yield for clusters of Co3O4 nano-sized crystals was about 1,600 times higher than for micron-sized particles, and the turnover frequency was about 1,140 oxygen molecules per second per cluster, which is commensurate with solar flux at ground level," notes Frei. (To view a video showing the evolution of oxygen, click here >> http://www.youtube.com/v/Ei4mwyjG3Vg). Click Image To Enlarge